|
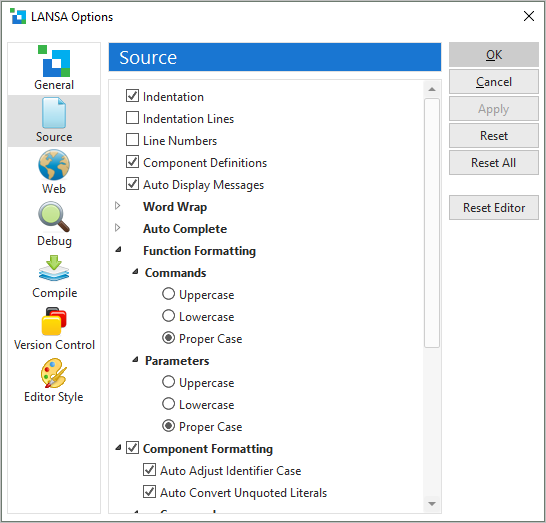
Indentation
|
Indents commands in the Source tab.
|
|
Indentation Lines
|
Indentation lines assist you in navigating the source code in the Source tab
|
|
Line Numbers
|
Turns line numbering on and off in the Source tab.
|
|
Component Definitions
|
Displays DEFINE_COM statements in RDML source code.
|
|
Auto Display Messages
|
Displays all error and warning messages expanded in the Source tab.
|
|
Word Wrap
|
None - Turns word wrapping off.
Simple - Line will break at any space.
Smart - Line wrapping keeps parameters on the same line.
|
|
Auto Complete
|
Off - If you choose this option, you will get no prompting in your Source code window to assist you in completing your code. The Assistant tab is still available.
|
|
Prompter - This is the most powerful of the options available to help you create our LANSA code. If you choose this option, a small dialog is open in the Source tab. This dialog offers items (commands, parameters) that appear to be close to those you are using.
|
|
Inline - If you choose this option, the Auto Complete facilities offered are the opportunity to select the most likely option in your Source code. This option is shown as part of your current line, rather than as a separate dialog.
Automatically completes text in the Source tab.
Refer to Auto Complete.
|
|
|
ShortCut - The keyboard shortcut for displaying Auto Complete can be either Ctrl + J or Ctrl + Space.
|
|
Audit Stamps
|
Name – displays the user name audit stamps in the Source tab.
Date – displays audit stamps dates in the Source tab.
Task Id – displays the audit stamps Task Id in the Source tab.
Refer to Task Maintenance in Visual LANSA Administration.
|
| Function Formatting
|
|
Commands
|
Format commands in:
- Proper case – initial uppercasing, for example Begin_Com
|
|
Keywords
|
Format keywords using:
|
|
Component Formatting
|
|
Adjust Identifier Case
|
Formats any identifier (variable/method/property/event-name) according to its definition.
If you define a method:
MthRoutine Name(MyMethod)
And you use it like this:
#COM_OWNER.mymethod
The formatter will replace it with:
#COM_OWNER.MyMethod
|
|
Auto Convert Unquoted Literals
|
RDML has always treated identifiers without quotes as upper-case strings. Therefore:
#STD_TEXT := hello
Is equivalent to:
#STD_TEXT := "HELLO"
Most people do not know this, and they make mistakes like:
#COM_OWNER.Caption := STD_TEXT
If you select the Auto Convert option, the formatter re-formats these literals as their equivalent uppercase string, so the formatter will change:
#STD_TEXT := hello
To:
#STD_TEXT := "HELLO"
This will help you not to write:
#COM_OWNER.Caption := STD_TEXT
any longer, because you will see it changed to:
#COM_OWNER.Caption := "STD_TEXT"
As soon as you leave the line.
|
|
Commands
|
Format commands in:
- Proper case – initial uppercasing, for example Begin_Com.
|
|
Parameters
|
Format parameters using:
|
|
System Values
|
Format system values using:
|